Fiber Length & Length Distribution
Cotton Fiber Length Analysis
Cotton are graded by HVI measurements on the following parameters:
- Fineness
- Fiber length & Length uniformity
- Strength & Elongation
- Micronaire
- Color
- Maturity
- Extraneous matter (trash, leaf & neps)
Fiber Length & Length Distribution
Fiber length
After fineness, length is the most important property of a fiber. The length of cotton is directly related to its spinning performance. Knowledge of fiber length is necessary to manufacture a yarn of specific size on ring spinning system and typically longer fibers are used to manufacture fine yarns. Longer fibers are generally more uniform, finer, and stronger than shorter ones. Yarn quality parameters such as strength, elongation, hairiness, and evenness are strongly correlated to the length of cotton fibers.
Depending on the variety, cotton fiber length varies from 0.9 inches to about 1.6 inches. It has a fineness (diameter) of 18 microns (18/1000 of a millimeter) and an average length of 1.1 inches. Long-staple cotton has a fineness (diameter) of less than 15 microns and an average length of over 1.125 inches long. Long staple cotton is produced in small quantities due to the high cost of growing and processing it.
Fiber Length Distribution
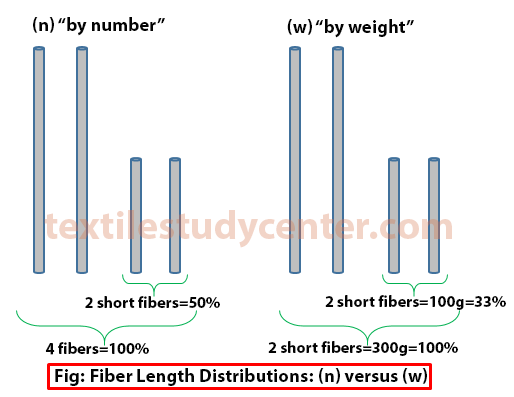
Length distribution is also an important consideration during the spinning process when fiber lengths are sufficiently long to meet yarn spinning requirements. It can be calculated by number or weight of fibers. The following schematic in figure below helps better understanding the difference between both distributions:
Four “ideal” fibers are shown with the same linear density or ‘weight’. For example, we assume all 4 fibers weigh together 300g:
By number, 50% of the fibers are short fibers.
By weight, 33% of all fibers are short fibers.
Both length distributions are used in the industry today. The by number distribution usually gives you more accurate results when optimizing your processes in spinning. The by weight distribution is used by mills that have been used to results of the comb sorter array methods such as the Suter-Webb-Array. However, it is really e spinning mill to decide what values they prefer to work with.
Advantage of longer average fiber length
In general,a longer average fiber length is to be preferred because it confers a number of advantages.
Firstly, longer fibers are easier to process.
Secondly, more even yarns can be produced from longer fibers because there are fewer fiber ends in a given length of yarn.
Thirdly, a higher strength yarn can be produced from them for the same level of twist. Alternatively, a yarn of the same strength can be produced but with a lower level of twist, thus giving a softer yarn.
Following are the most length distribution parameters in use in deferent countries:
Mean length (ML)
Upper half mean length (UHML)
Upper quartile Length (UQL)/Upper quartile mean length (UQML)
Effective length
Span lengths, SL
2.5% span length
50% span length
Modal length
Uniformity index (UI%) and
Uniformity ratio (UR%)
(0)
Fiber Length and Length Distribution




0 comments:
Post a Comment