Introduction to Marketing
What is Marketing?
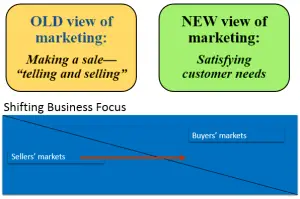
- Many people think of marketing as only selling and advertising. We are attacked every day with TV commercials, catalogs, sales calls, and e-mail pitches. However, selling and advertising are only the tip of the marketing iceberg.
- Broadly defined, marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and organizations obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging value with others. In a narrower business context, marketing involves building profitable, value laden exchange relationships with customers. Hence, we define marketing as the process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return.
Definition of Marketing:
- According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing Management is the analysis, planning, implementation and control of programs designed to bring about desired exchanges with target audiences for the purpose of personal and of mutual gain. It relies heavily on the adoption and coordination of product, price, promotion and place for achieving responses.“
- According to American Marketing Association (2004)– “Marketing is an organizational function and set of processes for creating, communicating and delivering value to customers and for managing relationships in a way that benefits both the organization and the stakeholder.“
- According to Eldridge (1970)– “Marketing is the combination of activities designed to produce profit through ascertaining, creating, stimulating, and satisfying the needs and/or wants of a selected segment of the market.”
Marketing Defined
- Marketing is the activity, set of instructions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Exchange as the focus
The following conditions must exist for a marketing exchange to take place:
►Two or more people or organizations must be involved, and each must have needs or wants to be satisfied. If you are totally self-sufficient, there is no need for an exchange.
►The parties to the exchange must be involved voluntarily.
►Each party must have something of value to contribute in the exchange, and each must be believe that it will benefit from the exchange.
►The party must communicate with each other. The communication can take many forms and may even be through a third party, but without awareness and information there can be no exchange.
Inventor & Innovator
Nature of Marketing
① Marketing is an Economic Function
Marketing embraces all the business activities involved in getting goods and services , from the hands of producers into the hands of final consumers. The business steps through which goods progress on their way to final consumers is the concern of marketing.
② Marketing is a Legal Process by which Ownership Transfers
In the process of marketing the ownership of goods transfers from seller to the purchaser or from producer to the end user.
③ Marketing is a System of Interacting Business Activities
Marketing is that process through which a business enterprise, institution, or organization interacts with the customers and stakeholders with the objective to earn profit, satisfy customers, and manage relationship. It is the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer or user.
④ Marketing is a Managerial function
According to managerial or systems approach – “Marketing is the combination of activities designed to produce profit through ascertaining, creating, stimulating, and satisfying the needs and/or wants of a selected segment of the market.”
According to this approach the emphasis is on how the individual organization processes marketing and develops the strategic dimensions of marketing activities.
⑤ Marketing is a social process
Marketing is the delivery of a standard of living to society. According to Cunningham (1981) societal marketing performs three essential functions:-
- Knowing and understanding the consumer’s changing needs and wants;
- Efficiently and effectively managing the supply and demand of products and services; and
- Efficient provision of distribution and payment processing systems.
⑥ Marketing is a philosophy based on consumer orientation and satisfaction
⑦ Marketing had dual objectives – profit making and consumer satisfaction
Scope of Marketing
① Study of Consumer Wants and Needs
Goods are produced to satisfy consumer wants. Therefore study is done to identify consumer needs and wants. These needs and wants motivates consumer to purchase.
② Study of Consumer behavior
Marketers performs study of consumer behavior. Analysis of buyer behavior helps marketer in market segmentation and targeting.
③ Production planning and development
Product planning and development starts with the generation of product idea and ends with the product development and commercialization. Product planning includes everything from branding and packaging to product line expansion and contraction.
④ Pricing Policies
Marketer has to determine pricing policies for their products. Pricing policies differs form product to product. It depends on the level of competition, product life cycle, marketing goals and objectives, etc.
⑤ Distribution
Study of distribution channel is important in marketing. For maximum sales and profit goods are required to be distributed to the maximum consumers at minimum cost.
⑥ Promotion
Promotion includes personal selling, sales promotion, and advertising. Right promotion mix is crucial in accomplishment of marketing goals.
⑦ Consumer Satisfaction
The product or service offered must satisfy consumer. Consumer satisfaction is the major objective of marketing.
⑧ Marketing Control
Marketing audit is done to control the marketing activities.
Marketing Management
►The art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them.
►Requires that consumers and the marketplace be fully understood.
►Aim is to find, attract, keep, and grow customers by creating, delivering, and communicating superior value.
Marketing managers must consider the following, to ensure a successful marketing strategy:
- What customers will we serve?
— What is our target market? - How can we best serve these customers?
— What is our value proposition?
Needs, Wants, and Demands
Need: State of felt deprivation including physical, social, and individual needs.
- Physical needs: Food, clothing, shelter, safety
- Social needs: Belonging, affection
- Individual needs: Learning, knowledge, self-expression
Want: Form that a human need takes, as shaped by culture and individual personality.
Demand
•Wants + Buying Power = Demand
Types of Demand
- Negative Demand
- No Demand
- Latent Demand
- Declining Demand
- Irregular Demand
- Full Demand
- Overfull Demand
- Unwholesome Demand
(0)
Introduction to Marketing





0 comments:
Post a Comment